A comprehensive custom LCD module RFQ must include application context, environmental conditions, display performance requirements, electrical specifications, mechanical constraints, and quality expectations to enable accurate quoting and successful development.
A custom LCD module RFQ must include these fields: application and use case, operating environment (temperature, humidity, vibration, chemicals), target display and optical stack requirements (active area, resolution, brightness/readability, viewing angles, cover lens treatments, bonding/air gap), electrical requirements (interface type, timing references, power rails, backlight and dimming), mechanical constraints (outline limits, mounting method, connector access, sealing/gasket), and quality/business requirements (cosmetic criteria, validation tests, target volumes, documentation, change control, lifecycle/EOL expectations).
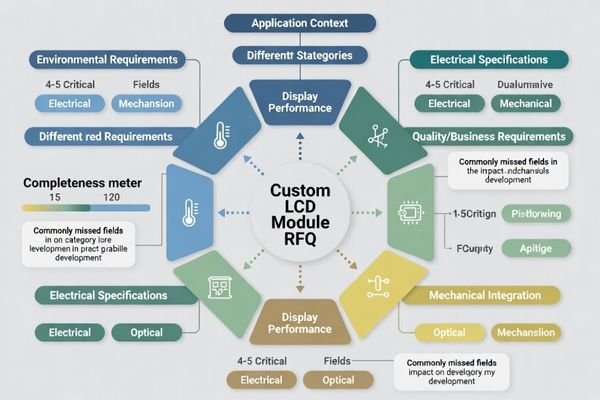
In LCD display module integration work at MEIDAYINGNUO, incomplete RFQs often create more project delays than complex technical requirements. Teams may focus on basic specifications while omitting the system context that drives optical design, mechanical integration, and electrical compatibility decisions. Comprehensive RFQ development1 reduces iteration cycles and enables accurate feasibility assessment from the first supplier engagement.
Why do incomplete RFQs delay custom LCD module development?
Incomplete RFQs force suppliers to make assumptions about critical design parameters, leading to misaligned development efforts and costly revisions.
Custom LCD module development requires engineering inputs that determine feasibility, risk, schedule, and production stability. Missing fields hide cross-domain conflicts such as brightness versus thermal limits, cover lens thickness versus optical performance, and interface timing versus cable length in noisy environments, forcing redesign after tooling or validation has started.
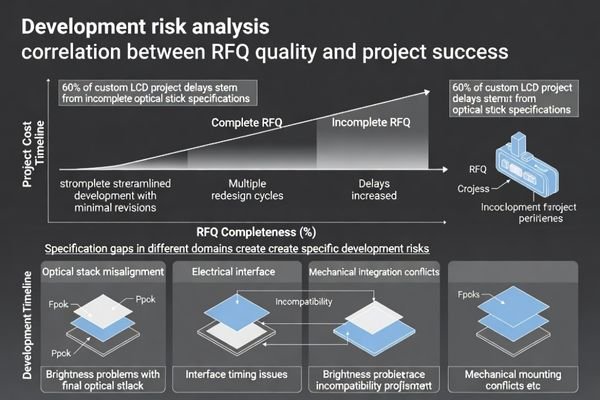
From an engineering standpoint, custom module development2 is simultaneous optimization across optical, electrical, mechanical, and manufacturing domains. When RFQ fields are missing, suppliers must either request clarifications or proceed with broad assumptions, both of which slow convergence on manufacturable solutions that meet system-level integration requirements.
Development Risk Factors
Incomplete specifications create hidden design conflicts that emerge during prototyping or validation phases when correction costs are highest and schedule impact is most severe.
Cross-Domain Integration Requirements
Custom modules require simultaneous consideration of optical stack design, electrical interface compatibility, mechanical mounting constraints, and manufacturing feasibility that incomplete RFQs cannot adequately address.
What application and environment details should the RFQ specify?
Application context and environmental conditions drive fundamental design decisions for materials, construction methods, and validation requirements.
Define use case context including end product type, installation location, and operator behavior patterns that affect viewing requirements. Specify operating and storage conditions including temperature range, humidity exposure, vibration expectations, and chemical contact scenarios because these directly influence material selection for polarizers, adhesives, and protective coatings.

Material compatibility failures often result from inadequate environmental specification during RFQ development. Adhesive delamination, polarizer degradation, and gasket failure modes3 can depend on specific temperature cycling, humidity exposure, and chemical contact scenarios that should be defined early to support correct material and construction choices.
Which display performance and optical stack parameters are essential?
Display performance requirements must address the complete optical stack and viewing experience rather than isolated panel specifications.
Specify target viewing experience including active area, resolution, content style, and effective readability in the final stack rather than raw panel specifications. Define brightness expectations, viewing angle priorities, acceptable color shift, and cover lens integration approach including thickness, surface treatments, and bonding strategy because these choices affect reflections, contrast, and serviceability.
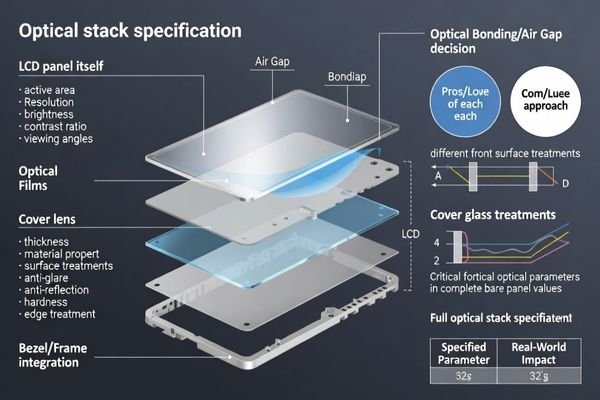
Specification gaps around cover lens integration and surface treatments are common sources of field issues. Glare control, reflection management, and contrast optimization depend on the complete optical stack design, so these requirements should be captured in the RFQ instead of being deferred until late-stage integration.
| Optical Parameter | Specification Approach | Integration Impact | Common Gaps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brightness | Effective readability in final stack | Power, thermal design | Raw panel numbers only |
| Viewing Angle | Direction priorities, acceptable shift | Optical stack design | Symmetric assumptions |
| Cover Lens | Thickness, treatments, bonding approach | Reflections, serviceability | Material selection only |
| Glare Control4 | Ambient conditions, reflection management | Surface treatments, bonding | Laboratory-only validation |
Comprehensive optical specification enables system-level optimization rather than component-level compliance that may not achieve application requirements.
What electrical, mechanical, and quality fields prevent integration surprises?
Electrical interface, mechanical integration, and quality requirements must address system-level compatibility and production requirements to prevent late-stage issues.
Include host platform context with interface type, timing parameters, power constraints, and backlight dimming requirements. Provide mechanical constraints including dimensions, mounting method, connector access, and gasket requirements. Specify quality expectations including cosmetic criteria, reliability validation needs, and lifecycle planning requirements for stable production.

Electrical and mechanical integration problems often emerge during system validation when correction requires significant rework. Power sequencing issues, interface margin problems, and mechanical stress failures are frequently driven by incomplete system-level inputs during RFQ development rather than component-level defects. For integration specification and validation planning support during RFQ preparation, engineering teams can contact info@lcdmodulepro.com.
Signal Chain Compatibility
Electrical specifications should address the complete signal path, including expected cable length and routing environment, grounding strategy, and EMI/ESD considerations that affect interface stability and long-term reliability.
Mechanical Integration Planning5
Mounting design, connector access, and serviceability requirements should be specified early to prevent stack-up conflicts and to enable practical field maintenance throughout the product lifecycle.
How should you structure a custom LCD module RFQ package?
RFQ organization should enable efficient supplier evaluation while providing complete technical information for accurate development planning and risk assessment.
Structure RFQ packages with executive summary, detailed technical specifications, supporting documentation, and explicit trade-off guidance. Begin with application context and non-negotiable constraints, followed by technical requirements organized by domain, then provide supporting materials and validation expectations to enable comprehensive supplier response.
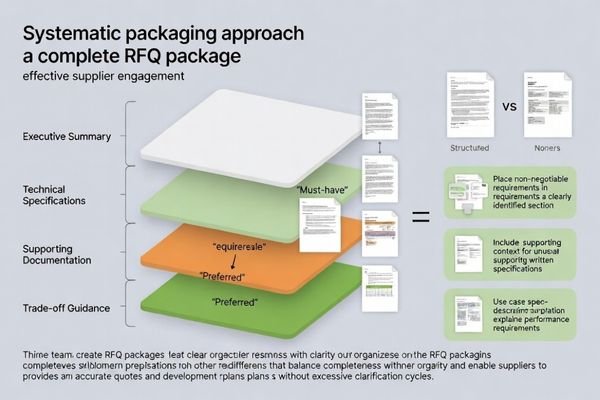
Successful packages balance completeness with clarity by organizing information hierarchically and making trade-offs explicit. Suppliers need sufficient context to propose optimal solutions while understanding which parameters are fixed constraints versus negotiable optimization targets.
RFQ Package Structure:
Executive Summary
- Application overview and market context
- Key performance requirements and constraints
- Target volumes and timeline expectations
- Non-negotiable requirements versus flexible parameters
Technical Specifications
- Optical stack requirements and front surface integration
- Electrical interface parameters and system compatibility
- Mechanical envelope and mounting constraints
- Environmental conditions and reliability expectations
Supporting Documentation
- Mechanical drawings or dimensional constraints
- UI mockups showing content density and style
- Cable routing and grounding considerations
- Validation requirements and acceptance criteria
- Must-have specifications versus preferred ranges
- Cost, schedule, and performance priority ranking
- Alternative approach evaluation criteria
- Change control and lifecycle planning expectations
This structure enables suppliers to provide accurate feasibility assessment, realistic scheduling, and appropriate risk mitigation strategies while identifying optimization opportunities that align with application priorities.
FAQ
What is the most common missing field in a custom LCD module RFQ?
The most common gap is the lack of system context—especially the final front stack concept (cover lens, surface treatments, bonding/air gap) and the real ambient light and viewing conditions. Without this, suppliers cannot predict readability or propose the right optical approach.
Should the RFQ include target specifications or acceptable ranges?
Ranges are usually better for custom development because they make trade-offs explicit and reduce redesign risk. Provide "must-have" constraints and "negotiable" ranges so the supplier can optimize cost, schedule, and reliability.
Do I need to provide mechanical drawings at the RFQ stage?
If CAD is not ready, provide key dimensions, keep-out zones, mounting method, and connector access constraints. Early mechanical constraints prevent stack-up conflicts that are expensive to fix after tooling.
How should I describe interface timing if I don’t have finalized parameters?
Provide the host platform type and what is known: interface family, target resolution/frame rate, expected cable length, and any prior reference design constraints. Ask the supplier to propose a timing set and validation plan with margin.
What should I include about backlight and power to avoid later instability?
State available power rails, current limits, dimming preference (PWM or analog), brightness use profile, and any sequencing constraints. This helps avoid flicker, startup issues, and EMI surprises during integration.
How can I reduce EOL risk when requesting customization?
Ask for lifecycle expectations, change notification practices, and critical-to-quality parameters, and request an approach for qualifying alternates. Treat lifecycle planning as part of the RFQ, not a post-launch reaction.
Conclusion
Comprehensive custom LCD module RFQ development requires systematic specification of application context, environmental conditions, optical stack requirements, electrical interface parameters, and mechanical integration constraints. Success depends on providing sufficient system-level information for accurate feasibility assessment while making trade-offs and priorities explicit. Understanding the relationship between specification completeness and development efficiency enables better supplier engagement and reduces iteration cycles that delay project completion.
MEIDAYINGNUO provides custom LCD display modules and engineering support, including RFQ optimization consulting, feasibility analysis support, and system-level integration planning. Our team helps translate application requirements into manufacturable specifications that address optical performance, electrical compatibility, mechanical integration, and lifecycle planning needs. Contact our technical team when custom LCD module requirements demand detailed specification development and feasibility analysis for successful project execution.
✉️ info@lcdmodulepro.com
🌐 https://lcdmodulepro.com/
-
Understanding RFQ development can help streamline your project processes and reduce delays. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into effective strategies for optimizing custom module development across various engineering domains. ↩
-
Exploring gasket failure modes can enhance your knowledge on ensuring reliable sealing in various applications. ↩
-
Understanding glare control techniques can significantly enhance optical performance and user experience. ↩
-
Exploring effective mechanical integration planning strategies can enhance product lifecycle management and serviceability. ↩
-
This link will provide insights on balancing specifications and priorities, crucial for successful project execution. ↩
