Selecting the right LCD module supplier goes far beyond comparing datasheets and prices. The supplier’s capabilities in quality control, engineering support, and long-term partnership determine whether your product succeeds in the market or faces costly redesigns and field failures.
Before choosing an LCD module supplier, check these 10 points: quality system and traceability, stable supply and lifecycle control, real optical performance capability, interface and customization engineering support, mechanical stack-up and tolerances, reliability testing and evidence, production capacity and yield control, documentation and change management, compliance and certifications, and after-sales support with RMA responsiveness.
These 10 checks work best as a supplier qualification framework: each item should end with concrete evidence you can review before committing to volume production.
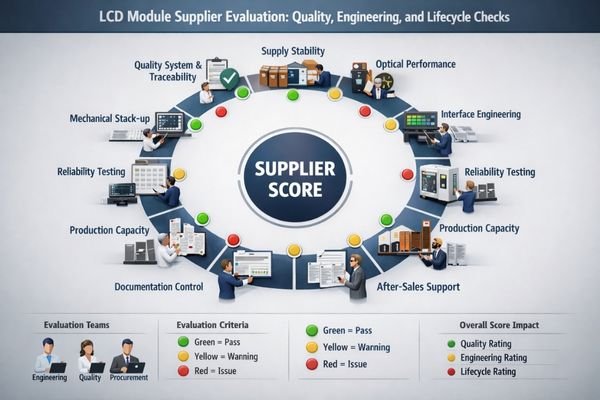
In supplier qualification, the most expensive problems often appear months after production ramps—when a minor material change shifts optical appearance, a yield drop triggers shortages, or an unclear interface baseline forces firmware workarounds. Strategic suppliers protect you not only with manufacturing capability1, but with disciplined process control, proactive communication, and repeatable engineering support that stays consistent as volumes scale and revisions evolve.
A thorough evaluation should confirm how a supplier prevents silent drift, how they communicate change, and how quickly they close the loop when issues occur. The goal is simple: keep early prototype performance repeatable at scale while reducing lifecycle risk across the full product timeline.
What counts as a "real" quality system, and how deep should traceability go?
A legitimate quality system provides consistent repeatability through documented processes and measurable controls.
A real quality system demonstrates defined inspection gates with measurable acceptance criteria, traceable material control from incoming components through finished goods, and the ability to correlate any field issue back to specific lots, process conditions, and test data.
Statistical Process Control Implementation
Modern quality systems should demonstrate statistical process control at key manufacturing stages, not just final inspection checkpoints. This includes incoming material verification with documented acceptance criteria, in-process monitoring of critical parameters like brightness uniformity and color coordinates, and final testing that validates both electrical and optical performance against specification limits.
Material Traceability Architecture2
Comprehensive traceability should enable correlation between any field failure and the specific material lots, process parameters, and test conditions present during manufacturing. This capability transforms quality incidents from broad investigations into targeted corrective actions, reducing both response time and the scope of potentially affected products.
Evidence to request: sample IQC/IPQC/OQC records, a lot trace report example, and a corrective-action report showing how a defect was isolated to a specific material/process lot.
How do you judge supply stability and lifecycle control before signing?
Supply stability encompasses component risk management, inventory strategies, and proactive change communication that prevents emergency situations.
Evaluate the supplier’s component sourcing strategy, buffer planning for critical parts, EOL/PCN notification processes, and their ability to provide alternative solutions when changes become unavoidable.
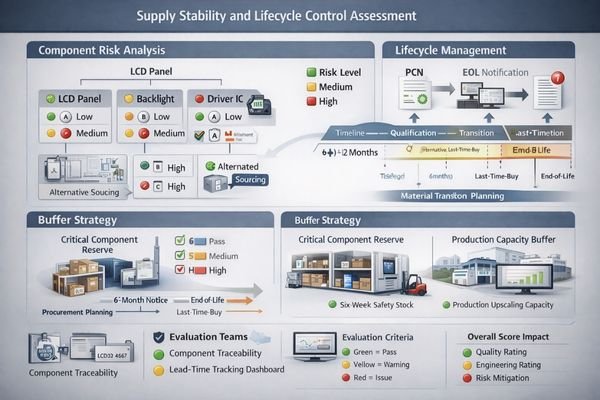
The most reliable suppliers maintain strategic inventory positions on critical components with long lead times or single-source risks, sized to the risk level of your program rather than a one-size-fits-all number. They should demonstrate documented relationships with multiple component suppliers for key materials like panels, backlights, and driver ICs, providing flexibility when upstream disruptions occur. Change notification discipline becomes critical for maintaining supply continuity—strong suppliers provide early warning of component changes or end-of-life events, complete with impact assessments and practical alternative material recommendations. This proactive approach enables planned transitions rather than emergency redesigns that can halt production and increase costs significantly.
Evidence to request: a PCN/EOL process template3, a recent PCN example with impact assessment, and a clear statement of lead-time assumptions and mitigation options for high-risk components.
Why is scenario-matched optical performance more important than a datasheet?
Optical performance under real-world conditions determines user experience and product differentiation in ways that laboratory specifications cannot predict.
Scenario-matched optical performance means the supplier understands your specific use case—indoor, semi-outdoor, or outdoor—and can control brightness uniformity, reflection behavior, and viewing angle consistency across production lots under those conditions.
Laboratory datasheet specifications typically measure performance under ideal conditions that rarely match actual deployment environments. Real applications involve cover glass combinations, touch panel integration, varying ambient lighting, and viewing angle requirements that significantly affect perceived image quality and readability. A capable supplier should provide optical validation4 using your actual front-stack configuration, including any anti-reflective treatments, touch sensors, or protective coatings that will be present in the final assembly. This testing should demonstrate not only peak performance but also the consistency of optical parameters across production batches, ensuring that early prototype performance remains achievable throughout volume production. Without this scenario-specific validation, teams often discover optical performance gaps late in development, leading to expensive redesigns or compromised user experience.
Evidence to request: optical validation results with your front stack (cover glass/touch/coatings), uniformity data, and a lot-to-lot consistency statement tied to controlled materials.
Can they support your interface, timing, and customization without destabilizing your product?
Engineering support quality directly impacts integration success, development timeline, and long-term product stability.
Strong engineering support means the supplier can maintain stable interface baselines while handling customization through controlled engineering processes, providing consistent timing parameters, voltage specifications, and initialization sequences across production batches.
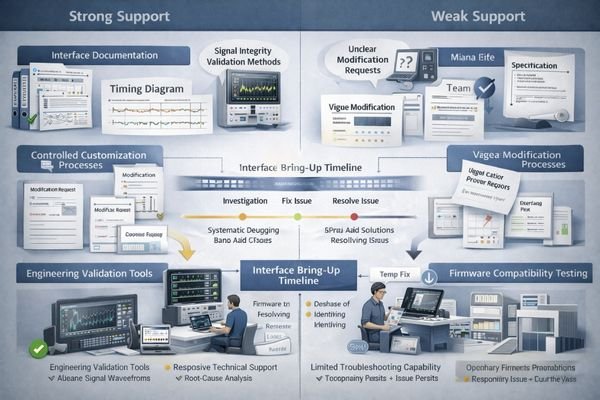
Interface stability requires disciplined parameter control5 across multiple dimensions: electrical timing specifications must remain within defined windows regardless of production lot variations, voltage level requirements should be clearly specified with appropriate margins, and initialization sequences must be documented with clear timing relationships. The supplier’s engineering team should demonstrate understanding of your system architecture and be capable of providing interface guidance that prevents integration problems during bring-up and scaling phases.
Customization capabilities should be evaluated through controlled engineering processes rather than ad-hoc modifications that can introduce instability. This includes the ability to modify timing parameters within safe margins, adjust interface configurations without affecting core functionality, and provide documentation updates that accurately reflect any changes made for your specific application. Poor engineering support often manifests as parameter drift between production lots, requiring firmware modifications or causing intermittent stability issues that are difficult to diagnose and expensive to resolve in the field.
Evidence to request: a timing/voltage baseline document, an initialization reference (as applicable), and an example of how a customization change was documented and controlled across revisions.
What mechanical stack-up and tolerance discipline prevents fit and cosmetic failures?
Mechanical precision affects both functional integration and aesthetic quality throughout the product lifecycle.
Mechanical discipline requires controlled drawings with clear datum references, specified tolerances for critical dimensions, and stack-up guidance that accounts for cover lens thickness, adhesive gaps, and assembly variation.
| Mechanical Aspect | Critical Requirements | Tolerance Impact | Validation Method | Failure Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Area Position | Datum Reference Control | ±0.1mm for UI Alignment | Coordinate Measurement | Interface Misalignment |
| Outline Dimensions | Enclosure Fit Tolerance | ±0.2mm for Mechanical Fit | Dimensional Verification | Assembly Interference |
| Connector Location | Cable Routing Clearance | ±0.15mm for Flex Management | 3D Stack-up Analysis | Connection Failures |
| Front Stack Height | Cover Glass Integration | ±0.05mm for Bonding | Layer Thickness Control | Optical Degradation |
| Mounting Features | Fastener Alignment | ±0.1mm for Hardware Fit | Fixture Validation | Mechanical Stress |
Many apparent "display failures" actually originate from mechanical tolerance accumulation that creates stress concentrations, optical path distortions, or connection reliability issues. Strong suppliers provide complete mechanical specifications including worst-case stack-up analysis and assembly guidance that prevents both immediate fit problems and long-term reliability degradation.
Evidence to request: mechanical drawings with datums and tolerances, an outline + active-area reference scheme, and a stack-up recommendation covering cover lens/touch thickness and adhesive gaps.
What reliability evidence should you demand for your environment and lifetime target?
Reliability validation must demonstrate performance margins under conditions that match or exceed your actual deployment environment.
Demand reliability testing results that cover your specific temperature range, duty cycle, humidity exposure, and mechanical stress conditions, with clear sample counts, test durations, and failure criteria.

Environmental testing should encompass the complete operating envelope your product will experience, including temperature cycling that stresses thermal expansion mismatches, humidity exposure that tests seal integrity and electrical insulation, and mechanical vibration or shock that validates structural durability. The supplier should provide test reports with sufficient sample sizes for meaningful confidence, with scope tailored to your risk level and application severity.
Backlight lifetime data becomes particularly critical for applications requiring consistent brightness over extended operating periods. This testing should include luminance decay curves under your specified operating temperature and duty cycle, with projections to your target lifetime based on appropriate acceleration models. The supplier should also demonstrate understanding of failure modes that could affect reliability, such as LED degradation mechanisms, optical film delamination risks, and driver circuit aging effects, providing margin analysis that supports specification compliance throughout the intended product lifetime.
Evidence to request: test reports with conditions and pass criteria6, long-run backlight stability data under relevant temperature/duty assumptions, and a failure-mode summary with preventive actions.
How can you verify production capacity, yield stability, and process control at scale?
Manufacturing maturity determines whether quality and delivery performance remain consistent as production volumes increase.
Production maturity is demonstrated through yield tracking by station and lot, documented process controls that prevent parameter drift, and statistical evidence of consistent quality across volume production.
- Yield Management Systems7: Suppliers should maintain real-time yield tracking with statistical analysis capabilities that identify trends before they become quality escapes, including yield by process station, defect categorization, and corrective action tracking
- Process Control Documentation: Critical manufacturing parameters must be monitored and controlled within specified limits, with automatic data collection systems that prevent human error and provide traceability for quality investigations
- Capacity Planning Methods: Production planning systems should demonstrate ability to scale capacity while maintaining quality standards, including equipment utilization optimization, workforce training programs, and supply chain coordination capabilities
- Quality Escape Prevention: Robust final inspection and testing protocols must catch defects before shipment, including automated optical inspection, electrical parameter verification, and statistical sampling procedures
Manufacturing scalability requires proven process control systems that maintain parameter consistency regardless of production volume fluctuations. This includes equipment calibration programs, operator training standards, and quality monitoring systems that provide early warning of process drift before customer impact occurs.
Evidence to request: yield trend samples (by station/lot), a description of critical process controls for optical/electrical consistency, and an example of how drift was detected and corrected.
What does good documentation, revision control, and PCN/ECR discipline look like?
Documentation discipline prevents miscommunication and ensures consistent understanding across engineering, purchasing, and manufacturing teams.
Comprehensive documentation includes controlled mechanical drawings, complete electrical specifications, detailed test procedures, and revision control systems that make all changes auditable and traceable.

Documentation Completeness Standards
Technical documentation should provide sufficient detail for successful integration without requiring extensive interpretation or additional clarification. This includes mechanical drawings with complete dimensioning and tolerance specifications, electrical interface definitions with timing diagrams and signal descriptions, and assembly instructions that address potential integration challenges.
Change Control Process Maturity8
PCN and ECR processes must provide adequate lead time and impact assessment for all material or process changes that could affect form, fit, function, or reliability. Strong suppliers maintain change advisory boards that evaluate proposed modifications, provide detailed impact analysis including qualification requirements, and coordinate implementation timelines that minimize customer disruption.
Evidence to request: a datasheet + drawing package with revision history, a PCN example, and a documented rule for what changes trigger re-qualification.
Which compliance, certification, and declarations should be non-negotiable for your market?
Compliance readiness protects market access and reduces regulatory risk throughout the product lifecycle.
Essential compliance capabilities include RoHS/REACH declarations, material composition documentation, and consistent certification packages that meet your customer audit requirements.
- Material Compliance Documentation: Complete material declarations including supplier chain transparency, restricted substance testing reports, and conflict mineral disclosures that satisfy regulatory and customer requirements
- Process Certification Standards: Quality management system certifications (ISO 9001) and environmental management compliance (ISO 14001) that demonstrate systematic approach to compliance maintenance
- Product Safety Declarations: Appropriate safety standard compliance for intended applications, including electrical safety, EMC considerations, and any industry-specific requirements relevant to your market segment
Compliance management should be treated as an integrated part of the supplier’s quality system rather than an administrative afterthought. This includes maintaining current certification status, providing timely updates when regulations change, and demonstrating understanding of compliance requirements specific to your target markets and applications.
Evidence to request: current RoHS/REACH declarations, material disclosure package format, and a compliance documentation checklist that matches your customer audit needs.
What after-sales engineering support and RMA capability will you actually get?
After-sales quality becomes the true test of supplier partnership when field issues require rapid resolution.
Strong after-sales support provides rapid response times, engineering-level failure analysis with clear evidence, disciplined corrective action processes, and traceability systems that can correlate issues to specific production lots.
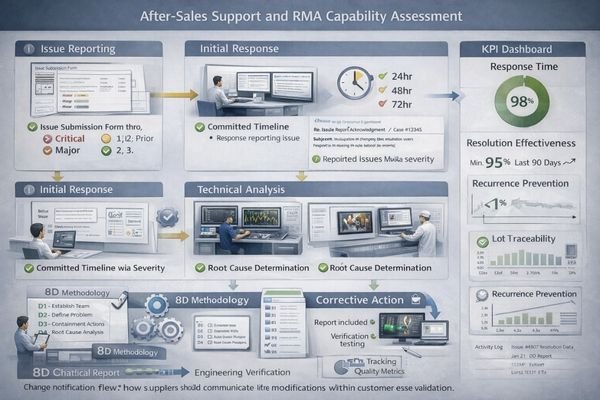
Response capability should include defined escalation procedures with committed response times for different severity levels, such as production-impacting issues versus non-critical technical questions. Engineering support depth becomes evident during failure analysis—qualified suppliers provide detailed technical investigation with evidence, measurements, and process correlation that identifies root causes rather than superficial symptom descriptions.
RMA processing efficiency affects both customer satisfaction and internal cost management. Effective systems include streamlined return authorization procedures, rapid initial assessment capabilities, and detailed failure analysis reporting that enables preventive actions. The supplier should maintain statistical tracking of RMA trends, demonstrate closed-loop corrective action implementation, and provide regular quality reports that show continuous improvement in field performance. This systematic approach to after-sales support protects your brand reputation by ensuring customer issues receive professional, thorough resolution rather than defensive or superficial responses.
Evidence to request: an RMA流程说明、样例8D/FA报告、以及针对生产批次的追溯闭环方式(lot correlation)说明。
Which MEIDAYINGNUO models are good starting points for supplier evaluation and pilot builds?
Pilot build model selection should match your target application characteristics to provide meaningful evaluation of supplier capabilities.
Our engineering approach focuses on helping customers validate complete supplier capabilities through representative pilot builds that stress real manufacturing processes and support quality systems.
| Application Category | Recommended Models | Evaluation Focus Areas | Key Validation Points | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-wide Bar Displays | BU156X, BU215X | Mechanical Consistency, Interface Support | Drawing Accuracy, Cable Management | Form Factor Complexity |
| Square Format Systems | SQ220S, SQ332S | Stack-up Control, Documentation Quality | Tolerance Analysis, Assembly Guidance | Integration Discipline |
| High Ambient Light | HB215X, HB238X | Optical Control, Thermal Management | Brightness Uniformity, Heat Dissipation | Environmental Performance |
| General Indoor Applications | SQ198H, BU173X | Process Maturity, Quality Systems | Yield Consistency, Defect Control | Manufacturing Scalability |
| Custom Form Factors | Contact for Analysis | Engineering Flexibility, Change Control | Customization Process, Documentation | Development Risk |
Successful pilot builds should validate not only technical performance but also the supplier’s ability to maintain consistency across multiple production lots, provide responsive engineering support during integration challenges, and deliver complete documentation packages that support both development and manufacturing phases. For comprehensive evaluation planning specific to your requirements, contact me at info@lcdmodulepro.com with your application details and evaluation timeline.
Conclusion
Choosing an LCD module supplier represents a strategic partnership decision that extends far beyond initial cost comparisons. The supplier’s capabilities in quality systems, engineering support, manufacturing consistency, and long-term collaboration determine whether your product achieves market success or encounters expensive development delays and field reliability issues.
MEIDAYINGNUO specializes in providing the engineering discipline, quality systems, and partnership approach that demanding applications require. Our comprehensive supplier evaluation process helps customers identify and validate LCD solutions that meet both immediate technical requirements and long-term business objectives. For detailed supplier evaluation support and pilot build planning, please contact our engineering team.
✉️ info@lcdmodulepro.com
🌐 https://lcdmodulepro.com
-
Exploring manufacturing capability can reveal how it affects production efficiency and product reliability. ↩
-
Exploring Material Traceability Architecture can reveal how to effectively link quality incidents to specific materials, improving corrective actions. ↩
-
Exploring a PCN/EOL process template can provide insights into managing component changes and ensuring supply continuity. ↩
-
Understanding optical validation is crucial for ensuring that your display meets performance standards in real-world conditions. ↩
-
Understanding parameter control is crucial for maintaining system stability and performance, making this resource invaluable for engineers. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will help you understand the essential elements of test reports that ensure product quality and compliance. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how effective yield management can enhance production efficiency and quality control. ↩
-
This resource will provide insights into enhancing change control processes, ensuring better management of modifications and their impacts. ↩
